Figure 2
From: Kelch proteins: emerging roles in skeletal muscle development and diseases
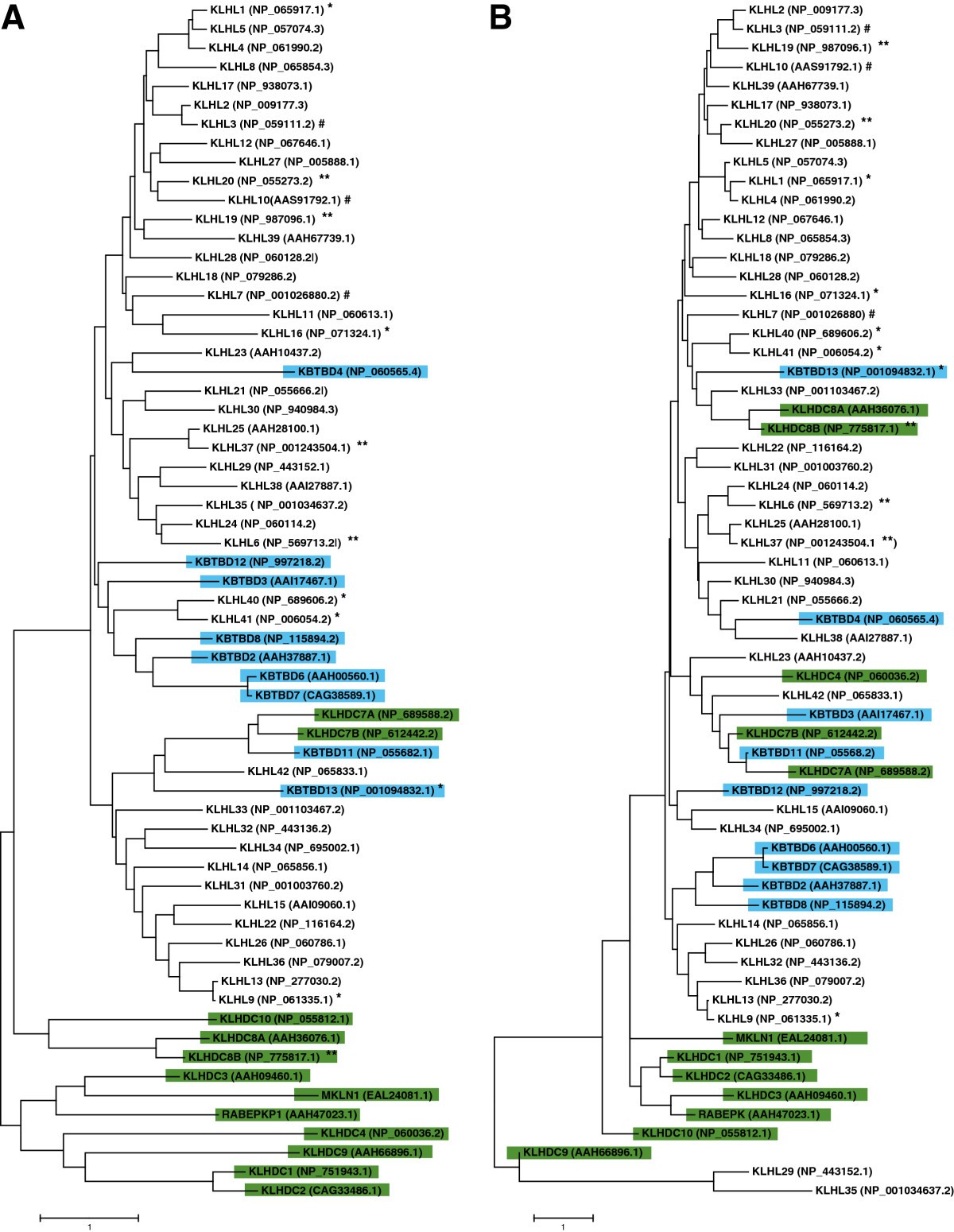
Phylogenetic analysis showing relationships between human Kelch protein family members. (A) Phylogenetic tree of full-length amino acid sequences of human proteins were aligned. (B) Phylogenetic tree of amino acid sequences of Kelch domains. Phylogenetic trees were constructed by maximum-likelihood method using BLOSUM matrix in MEGA 6.06. Reference sequences used for alignments are indicated at right of each protein name. Blue highlighting indicates KBTBD subfamily members; green indicates KLHDC subfamily members. *, proteins involved in neuromuscular diseases; **, family members implicated in cancer; #, proteins whose defects cause other inherited diseases (Table 2). Scale bars indicate relative distances and represent the degree of differences between the sequences.